SOURCE :
( ) MODERN POSITIONAL WARFARE AND HOW TO WIN IN IT : https://infographics.economist.com/2023/ExternalContent/ZALUZHNYI_FULL_VERSION.pdf
UDC 355
MODERN POSITIONAL WARFARE & HOW TO WIN IN IT
Valerii Zaluzhnyi
Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces of Ukraine, Kyiv, Ukraine
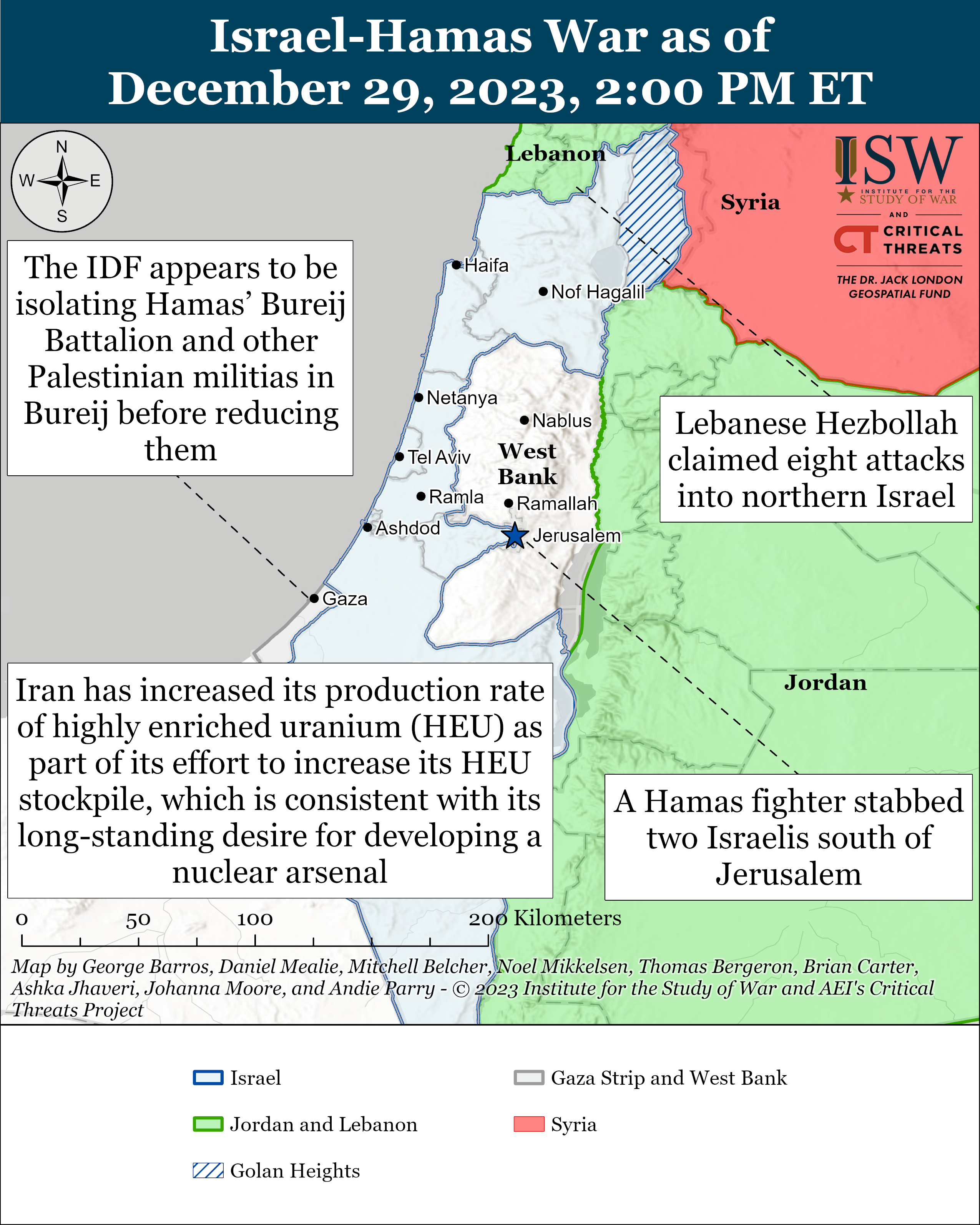
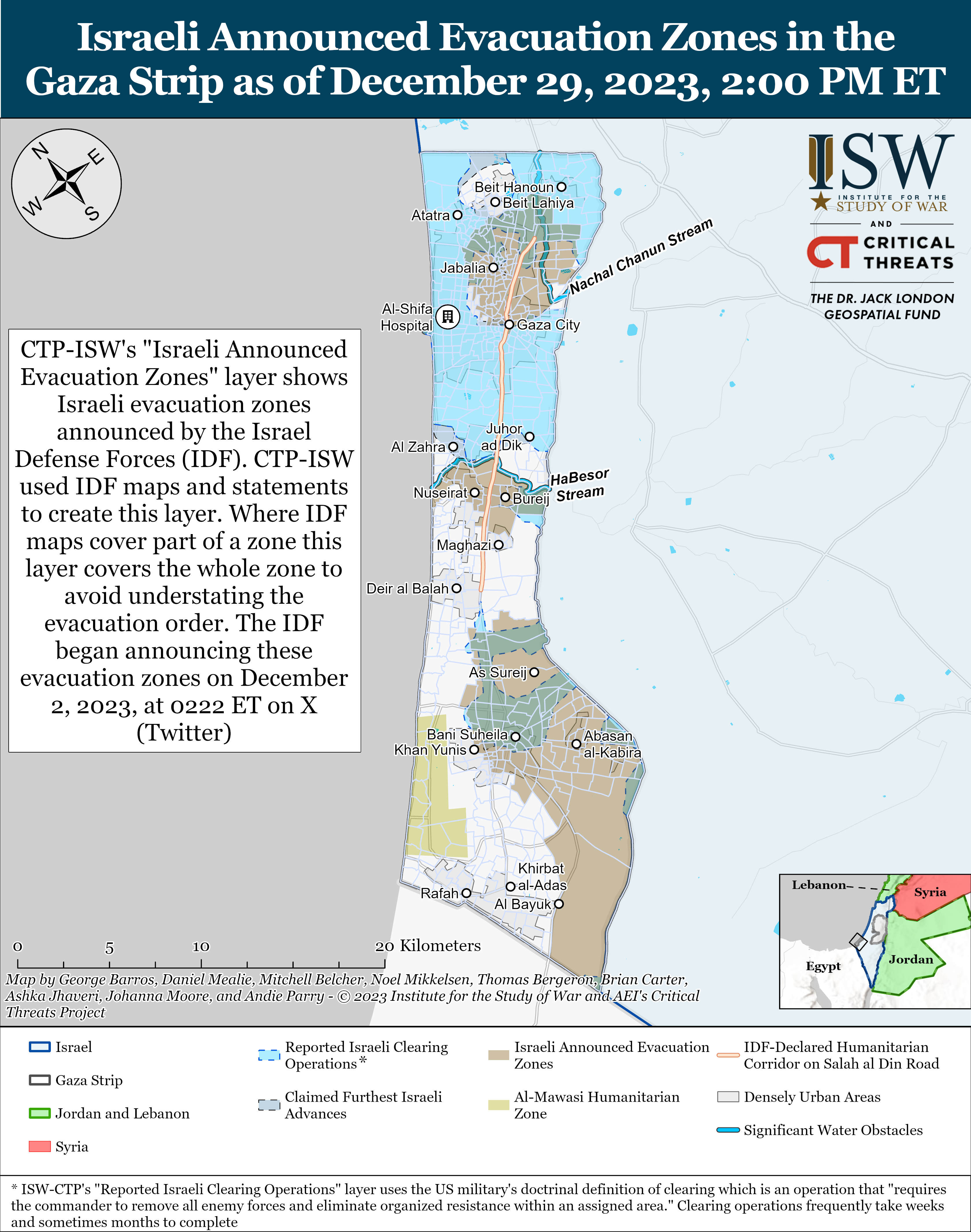
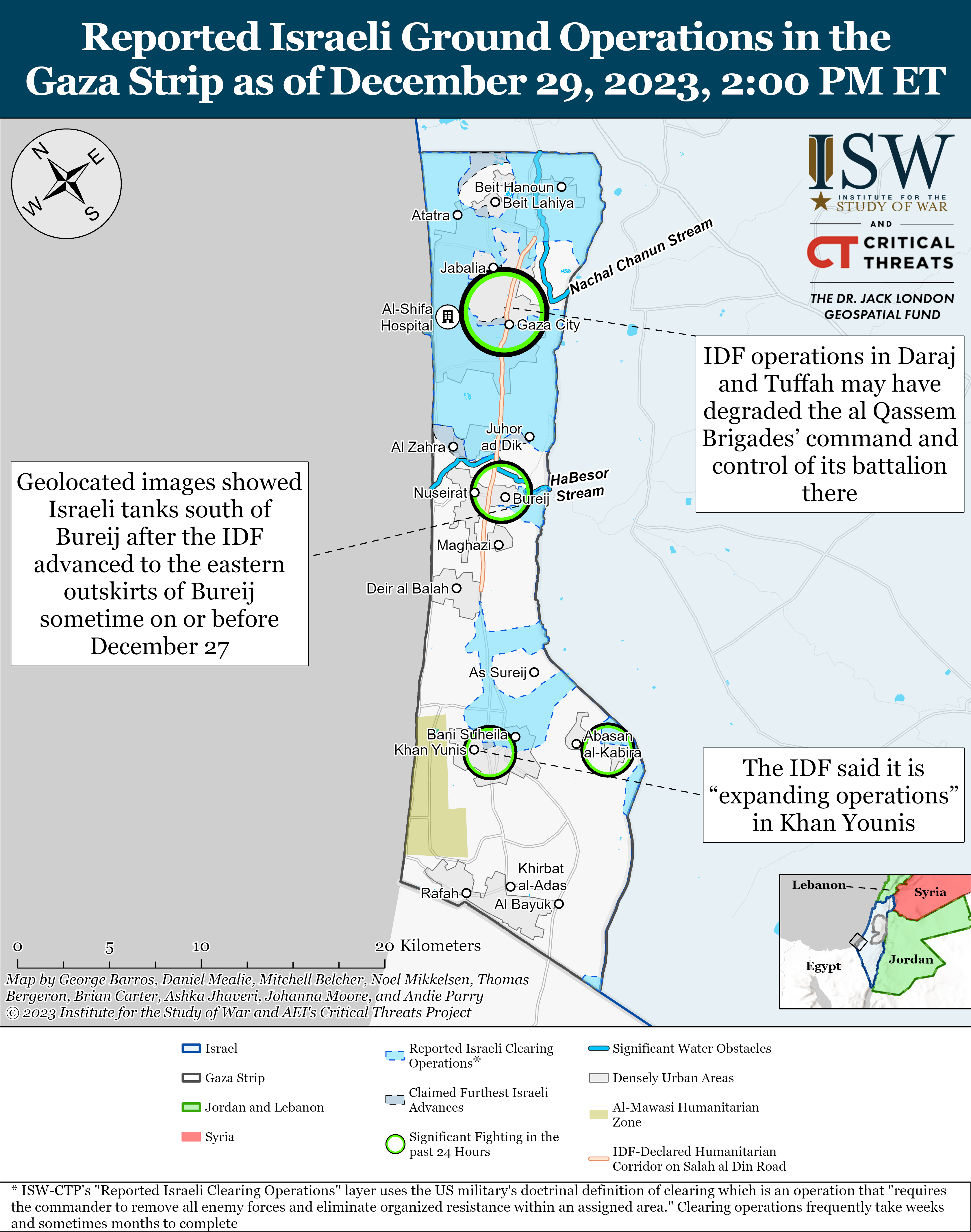
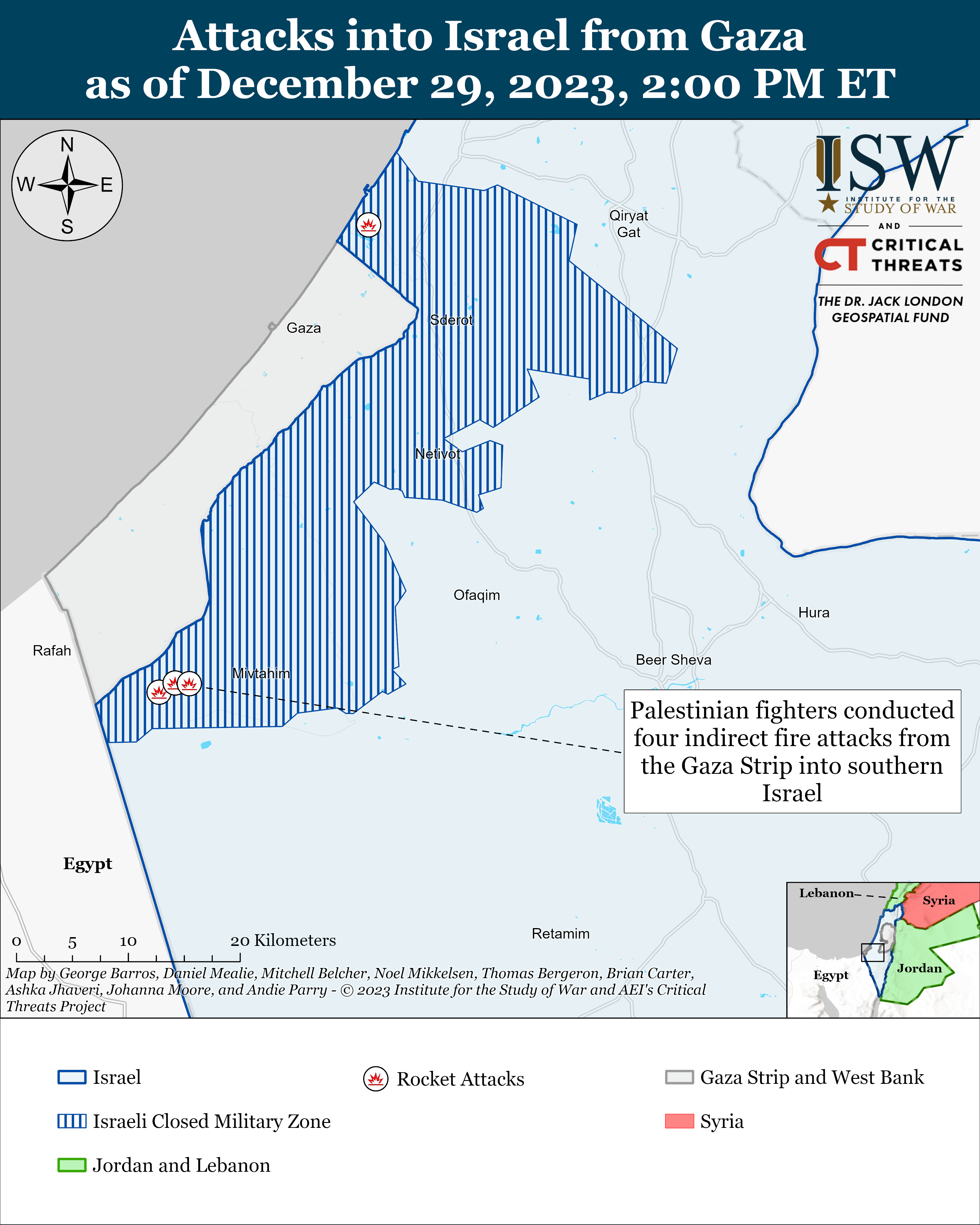
Having launched the large-scale armed aggression against Ukraine on February 24, 2022, the Russian federation provoked the beginning of an unprecedented global security crisis, the largest since the end of the Second World War. Russian great-power chauvinism multiplied by sick imperial ambitions gradually turns the military conflict it began in the centre of Europe into an armed confrontation between democratic and authoritarian political regimes with the prospect of its spread to other regions of the planet with similar geopolitical models (Israel and the Gaza Strip, South and North Koreas, Taiwan and China, etc.). The insufficient effectiveness of the existing global political regulatory mechanisms, primarily the UN and the OSCE, leaves Ukraine no choice but to restore its territorial integrity after the large-scale armed aggression within the internationally recognized borders of 1991, exclusively by military force, in which its Armed Forces (AF) play a decisive role.
Having entered the war with a stronger enemy, which has a lot of weapons and a much greater mobilization capabilities, Ukraine was not only able to stop it, but also to conduct a successful counteroffensive in 2022 and stave the enemy off along many axes. The people of Ukraine have demonstrated their willingness not in words, but in deeds to lay down their soul and body for their freedom. However, due to many subjective and objective reasons, the war at the present stage is gradually moving to a positional form, a way out of which in the historical retrospect has always been difficult for both the Armed Forces and the state as a whole. At the same time, the prolongation of a war, as a rule, in most cases, is beneficial to one of the parties to the conflict. In our particular case, it is the Russian federation, as it gives it the opportunity to reconstitute and build up its military power. Therefore, the issues of understanding the causes of such a situation, finding possible ways out of it and changing the nature and course of this war in favor of Ukraine are of particular relevance in modern conditions.
An analysis of the current situation in which the Armed Forces of Ukraine and other components of the state Defence Forces are placed shows that in order to find a way out of the positional form of warfare, it is necessary to: (a) gain air superiority; (b) breach mine barriers in depth; (c) increase the effectiveness of counter-battery; (d) create and train the necessary reserves; (e) build up electronic warfare (EW) capabilities. Therefore, the determination of the reasons for the transition of hostilities to the positional form and the search for possible ways out of this situation should obviously be carried out according to these main components. It should be noted that the above-mentioned components in no way level the role and place of missiles and ammunition, artillery systems, missile systems, electronic warfare, other types of weapons and equipment provided by partners. They only complement them in the context of increasing the capabilities of the Defence Forces through new technological solutions and innovative approaches on a way out of the positional crisis on the line of contact. Let's consider these reasons in more detail.
Reasons for the transition of hostilities to the positional form.
As for gaining air superiority.
Modern art of war involves gaining air superiority to successfully conduct large-scale ground operations. This is reflected both in the doctrines of NATO armed forces and in the governing documents of the armed forces of the Russian federation.
The Armed Forces of Ukraine entered the war with 120 tactical aircraft, out of which only 40 were considered to be technically suitable for utilization, and 33 medium and short-range anti-aircraft missile battalions, of which only 18 had fully serviceable equipment. Due to the material and logistical assistance of the Partner Nations, Ukraine has strengthened its aviation and air defence system. In particular, fighter and attack aircraft, as well as Soviet-made helicopters, were received. The number of anti-aircraft missile systems was significantly increased mainly due to Western-made assets, in particular, "Martlet", "Starstreak", "Javelin", "Piorun", "Mistral", "Stinger", "Grom" man-portable air-defence systems, "Gepard" self-propelled anti-aircraft guns, "Skynex" air defence gun systems, "Avenger", "Stormer", "Patriot", "Hawk", "IRIS-T", "NASAMS", "SAMP-T", "Crotale-NG" air defence systems. Due to this, since the beginning of the large-scale armed aggression, the Russian federation has lost a number of aircraft that roughly corresponds to the number of aircraft of one air army, and helicopters – about 13 regiments (brigades) of army aviation. In addition, the losses of enemy air defence systems of various types already exceed 550 pieces. Despite such losses, today the enemy continues to maintain significant air superiority, which complicates the advance of our troops and is one of the key factors that transforms the nature of hostilities into a positional form.
According to various assessments, at the end of 2023, the enemy may augment the number of aircraft by building new attack aviation squadrons, so special attention should be paid to this circumstance. But, despite the significant quantitative and qualitative superiority of the enemy in aviation and air defence, it cannot convert it into complete dominance in the air due to the successful work of our elements of direct air defence cover of troops, which constantly increase the number of the engaged enemy air attack weapons. This leads to the fact that the enemy does not feel calm in the skies of Ukraine, his aviation tries not to enter the kill zone of our anti-aircraft defences and utilizes air assets mainly from long ranges, which significantly reduces their effectiveness. Instead, the enemy's unmanned aerial vehicles come to the forefront, which have taken over a significant part of the tasks of manned aviation in terms of aerial reconnaissance and air strikes.
As for mine barriers breaching in depth.
The next prerequisite that transforms the nature of current hostilities into a positional form is the widespread use of mine barriers by both the enemy and our troops. Let's consider the situation with the capabilities to breach such barriers by our troops.
As of February 24, 2022, the Armed Forces of Ukraine had a limited capabilities package designed for breaching mine barriers. There were technically outdated pieces of equipment in service. Due to Western partners in the course of hostilities, it was possible to slightly augment the capabilities of engineer units (elements) on breaching using such assets as M58 MICLIC, Wicent 1, NM189 Ingeniorpanservogn, but given the unprecedented scale of these barriers, even such capabilities are objectively lacking.
Today, the enemy mine barriers along particularly important axes have a high density and reach a depth of 15-20 km. Their cover is conducted by reconnaissance UAVs, which effectively detect our obstacle-clearing detachments (teams) and target fire at them. In case of successful mine barriers breaching, the enemy quickly restores minefields in these areas by such engineering system of remote mine-laying as "Zemledeliye". At the same time, the Armed Forces of Ukraine are no less effective in using mine barriers and reconnaissance and fire complexes to detect and destroy the enemy`s engineer equipment for demining.
https://youtu.be/iiM4HEsxLUI
This condition leads to the fact that the offensive operations of both parties occur with significant difficulties and large losses of materiel and personnel.
As for counter-battery.
In the Russian-Ukrainian war, as in the wars of the past, the role of missile forces and artillery in fires remains quite significant, and depending on the conditions, axes and areas of operations varies from 60 to 80% of the total volume of tasks executed. The success of the troops' operations directly depends on the effectiveness of strikes and fire, so the "hunt" for the enemy's fire is a priority for both parties. Counter-battery is becoming an important component of the armed confrontation. And despite the statements of some so-called "military analysts", various publications, including in the russian media, regarding the gradual weakening of russia, we have no right to belittle the importance and capabilities of russian weapons, its ISR (intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance) and countermeasures, the ability of the military-industrial complex of the aggressor state to supply the troops with a significant number of both outdated and modern weapons and equipment. We must realistically assess threats, analyse experience, and draw conclusions.
Immediately after receiving Western missile and artillery weapons, the Armed Forces of Ukraine gained a significant superiority and significant success in counter-battery. Thus, precision guided munition e.g. Excalibur (155 mm shell) proved to be quite effective in the fight against self-propelled artillery and counter-battery radars. However, over time, their capabilities have significantly decreased, since the targeting system (using GPS) is very sensitive to the influence of enemy electronic warfare, which leads to a loss of precision of ammunition.
The enemy quickly learned to apply new tactics: dispersal (by guns); fire from the maximum range; use of new electronic warfare assets (the“Pole 21” electronic countermeasure system), etc. Also, the enemy quite widely and effectively began to use the Lancet loitering munition with target “illumination”, the Orlan, Zala UAVs and others for counter-battery, countering which is quite difficult.
In order to maintain and increase the duel superiority, the russians, through the use of outdated artillery systems (D-1, D-20, etc.), significantly increased the artillery density and its ability to massively use conventional ammunition. The enemy has also increased the production and intensity of the use of 122 mm Krasnopol precision guided munition, which is aimed at targets by target illumination with a rangefinder from ground-based observation posts.
As a countermeasure to the enemy, we were forced to utilize rocket artillery systems e.g. "HIMARS" to defeat his artillery. However, a significant part of the existing set of missiles was utilized for hitting these targets (artillery, MLRS, etc.). Currently, we have managed to achieve a notional parity with the numerically prevailing enemy artillery due to a smaller number of higher-quality (accurate) fires.
As for creation and preparation of the necessary reserves.
Compared to Ukraine, the russian federation has almost three times more mobilization human resources. Having failed to succeed in the initial period of the war, the enemy began a partial mobilization by the composition of the armed forces of peacetime in September 2022, which continues to date. But he fails to take advantage of the mobilization of human resources to create a significant superiority in the combat strength of task forces directly fighting against Ukraine.
The main reasons for this state are political, organizational and motivational in nature. Thus, on the eve of the presidential election, the president of the russian federation, putin, is afraid to conduct a general mobilization in connection with the possible risks of growing social tension in the state and turning it into a political crisis. The enemy has limited capabilities to train mobilized citizens and provide them with the necessary weapons and equipment. Due to significant losses of personnel, the civilian population of the russian federation seeks to evade conscription and participation in hostilities.
At the same time, it should be taken into account that despite the fact that the command of the Armed Forces of Ukraine is constantly working to improve the procedure for creating and preparing reserves, some issues remain problematic. In particular, we have limited capabilities to train reserves on our own territory, since the enemy has the ability to launch missile and air strikes on training centres and training grounds. The prolonged nature of the war, limited opportunities for the rotation of soldiers on the line of contact, gaps in legislation that seem to legally evade mobilization, significantly reduce the motivation of citizens to serve with the military. We are aware of these issues, we see ways to solve them and are constantly working on it. Thus, this leads to the lack of Ukraine's ability to achieve superiority over the enemy in reserves by increasing their number.
As for electronic warfare.
Even before the events of 2014, the military and political leadership of the russian federation paid considerable attention to the development of electronic warfare. An illustrative example of this is the creation in 2009 of a separate branch of the armed forces of the russian federation – the electronic warfare troops. In addition, as part of the russian armed forces, a powerful air component of electronic warfare has been created, which ensures the effective employment of troops (forces) and high-precision weapons. The enemy adopted about 60 types of modern electronic warfare equipment, which have better characteristics, high mobility, increased security, short set-up and tear-down time, the introduction of new technical solutions, automation tools, special software, etc. Almost the entire fleet of obsolete equipment has been updated.
The main advantages of russian electronic warfare equipment also include the establishment of serial production of the so-called "trench electronic warfare" ("Silok", "Piton", "Harpoon", "Piroed", "Strizh", "Lisochok"), which the tactical level of the russian troops is saturated with. Despite the fact that since the beginning of large-scale armed aggression, the enemy has lost a significant part of this equipment, today it continues to maintain a significant electronic warfare superiority. Along the Kupyansk and Bakhmut axes, the enemy actually established a layered electronic warfare system, the elements of which constantly change their location.
As for the Armed Forces of Ukraine, by 2022, such modern electronic warfare assets with UAVs such as "Bukovel-AD", "Enclave", "Khmara", "Nota" were adopted, which later proved themselves well in combat. But despite this, at the beginning of the war, about 65% of jamming stations types in units (elements) of the Armed Forces of Ukraine were produced by the former Soviet Union, and there were only 25 new ones.
Given the limited capabilities of the domestic defence-industrial complex, the build-up of EW capabilities was carried out at the expense of international military material and logistical assistance, by obtaining systems (assets) of detection and electronic warfare against UAVs, anti-drone guns, tactical mobile direction-finding systems, EW systems with on-board radar stations, etc.
To date, the capabilities to counter enemy high-precision weapons (guided missiles, UAVs) are being increased by deploying the "Pokrova" nationwide EW system with the possibility of replacing the satellite radio navigation field ("spoofing"), suppressing satellite radio navigation along the entire line of contact and in most parts of Ukraine. The development and implementation of elements of situational awareness systems into command and control processes is also under way: "Graphite" - for automated transmission and display of data about the flight of small UAVs; "Quartz" - for collecting, processing, displaying data and managing radio-electronic assets. At this time, we have practically achieved a parity in the EW tasks performance, which significantly complicates the possibility of achieving superiority by both the armed forces of the russian federation and Ukraine, when employing weapons and troops in general.
Thus, relying on the strategic superiority in military, economic, human, natural resource and scientific potential and relatively appropriate conditions for its implementation, the occupying armed forces are still not able to fully implement the plans of the russian general staff. At the same time, it should be noted that despite this, countermeasure to the achievement of military-political objectives by the aggressor state comes at a high cost for Ukraine and its Armed Forces. The above is especially acute in the current course of counteroffensive actions in the summer-autumn period. Thus, de facto, the Armed Forces of Ukraine and other components of the Security and Defence Forces involved in repelling armed aggression, practically along the entire line of contact between the parties and in the border areas with the russian federation, faced the need to overcome the military parity problem. First of all, its existence is stipulated by the reasons related to parity in the air, minefields, counter-battery and electronic warfare, and the creation of reserves.
Ways to overcome the positional nature of hostilities.
The need to avoid the transition to a positional form of hostilities, such as the "trench war" of 1914-1918, necessitates the search for new and non-trivial approaches to breaking the military parity with the enemy. The main idea of the way out of the current situation can be presented illustratively in the picture.
As for gaining air superiority:
- simultaneous en-masse use of cheap unmanned aerial target simulators and attack UAVs in a single combat formation in order to overload the enemy's air defence system, mislead the enemy about the number of real targets in the raid and expose elements of the enemy's air defence system;
- hunting down enemy UAVs with the help of our own hunter drones with trap nets on board in order to directly eliminate a destructive threat of materiel and personnel on the battlefield by kamikaze drones;
- use of radiation simulators of the medium-range anti-aircraft missile system to target illumination stations in close proximity to the contact line in order to reduce the effectiveness of the use of glide guided bombs against our troops when assuming offensive (due to the fact that carrier aircraft will launch guided bombs from the maximum possible ranges) and reduce the manned aviation intensity due to the pilots' refusal to conduct sorties;
- blinding of thermal imaging reconnaissance equipment and UAVs targeting with stroboscopes at night in order to complicate (prevent) strikes on the positions of troops (pieces of weapons and equipment) at night using UAVs equipped with thermal imaging equipment;
- en-masse use of electronic warfare assets (small and portable jamming transmitters, anti-drone guns, etc.) along the contact line of the parties to counter enemy UAVs in order to increase the ground forces protection from enemy UAVs.
As for counter-battery:
- building up local GPS fields to improve the operation of precision guided munition navigation tools;
- increasing the share of tasks on counter-battery, which are solved by reconnaissance and fire complexes based on kamikaze drones;
- use of counter-battery assets in combination with measures to mislead the enemy;
- increasing the capabilities of artillery reconnaissance equipment provided within the framework of international materiel and logistical assistance, through the use of non-standard settings.
As for mine barriers breaching in depth:
- use of LiDAR scanning sensors to obtain situational information on breaching on the ground; the “Rosy” smoke protection systems to conceal the activities of obstacle-clearing detachments (teams) from enemy ISR and fires; damaged equipment (without crews), which retained its manoeuvre capabilities;
- use of jet engines of decommissioned aircraft, water monitors (water cannons) or industrial water monitors, cluster artillery munition for breaching mine barriers that are installed without being dug in the ground;
- use of a mini tunnel excavator with a drill, Rapid Burrowing Robot (RBR), empty hoses for the injection of gaseous or liquid explosives, missiles with a fuel-air explosive for breaching mine barriers;
- use of anti-drone guns to counter enemy reconnaissance UAVs, which will increase the level of obstacle-clearing detachments (teams) concealment while breaching mine barriers.
As for creating own reserves and combating enemy ones:
- introduction of the "Oberih" Unified State Register of draftees, persons liable for military service and reservists into the activities of the command and control bodies;
- attracting more citizens of Ukraine to the military reserve;
- creation of an automated control system and accounting of training of Ukrainian citizens for military service and national resistance;
- expanding the list of categories of Ukrainian citizens with whom training for military service and national resistance is conducted;
- introduction of combat internship practice;
As for electronic warfare:
- introduction into the command and control processes of elements of the "Pokrova", "Graphite", "Quartz" situational awareness systems, as well as data exchange gained from Defence Forces ISR assets (systems);
- increasing the capabilities to monitor the current electronic situation in the areas of combat operations through the use of the capabilities of Partner Nations. In particular, we need to provide the possibility of expanded access to data from air, sea and space assets of signal intelligence;
- increasing the capabilities for conducting electronic warfare from UAVs during assault operations by combined arms elements;
- organization and conduct of counter-EW measures to detect, recognize, isolate and defeat the sources of electronic radiation of the enemy;
- search for opportunities to increase the production of electronic warfare systems with the "Bukovel- AD" UAVs on the territory of Ukraine and abroad;
- streamlining the use of "trench electronic warfare", which comes to the forces from volunteer organizations, in order to exclude cases of suppression of their own UAVs ("friendly fire");
- improvement of existing and development of new domestic EW systems, taking into account the prospect of conducting "electromagnetic warfare" throughout the "electromagnetic spectrum", which covers a much wider frequency range (from γ-radiation to terahertz radiation).
Command and control.
Improving the effectiveness of command and control is essential in the process of implementing the proposed ways out of positional warfare. This can be done through the widespread use of modern information technology in the command and control system, which will ensure: the formation of a single information environment; creation of conditions for information superiority; effective coordination of the activities of subordinate troops (forces). As a result, this will allow to get ahead of the enemy in matters of situational awareness and make decisions faster and, in general, ensure the achievement of a goal of an operation in terms of positional warfare. The key components that will influence the achievement of superiority in situational awareness are the processes of organizing communications, intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance.
Logistics Support.
One of the determining factors that significantly impacts the success of the implementation of the proposed ways to change the nature of the war and achieve goals is the rational organization of logistics support for the state Defence Forces.
Repelling the full-scale armed aggression of the enemy, conducting defensive and counteroffensive operations require a huge number of resources: human, mobilization, financial, materiel, etc. At the same time, the experience of the russian-Ukrainian war testifies to the actualization of almost forgotten concepts, for example, such as the accumulation of stocks of missiles and ammunition, and other logistics assets. After the end of the Cold War, the collapse of the Soviet Union and the Warsaw Pact states, this concept lost its relevance, but today it has become important both for the enemy and for our state.
The russian armed forces spend a large number of missiles and ammunition, but it should be recognized that some preparations for the war were done, so russia at this time retains and is able to maintain a superiority in weapons and equipment, missiles and ammunition for a considerable time, while the capabilities of the military industry are increasing, despite the introduction by the world's leading countries of unprecedented sanctions against the aggressor state.
The Armed Forces of Ukraine are provided with extensive materiel and logistical assistance by Partner Nations, however, given the increased intensity of average daily missiles and ammunition consumption, it is not possible to accumulate these funds in the required volumes since large armed forces are deployed, so all logistics assets provided within the framework of material and logistical assistance are distributed among forces according to the priority principle. Partner Nations and NATO member countries are currently dramatically increasing the production capacity of weapons and ammunition, but this process is quite long. According to various assessments, it takes at least a year to deploy large-scale production of weapons and equipment, missiles and ammunition, and other logistics assets, and in some types – two years.
To continue the effective destruction of enemy warehouses, disruption of supply chains and an increasing trucking distance for ammunition and other logistics assets, the Armed Forces of Ukraine need to adopt missiles with an increased range, preferably of their own production.
The main ways to improve the efficiency of logistics support are: development and capacity building of the Ukrainian defence industry; creation and development of an asymmetric arsenal of weapons and equipment in Ukraine; creation, production and deployment of new weapons. At the same time, when planning and organizing logistics support, it is necessary to take into account the enemy's ability of fire effects on the mobile and stationary components of logistics support assets of troops (forces).
Key takeaways.
The transition of the war to a positional form leads to its prolongation and carries significant risks for both the Armed Forces of Ukraine and the state as a whole. In addition, it is beneficial to the enemy, who is trying in every possible way to reconstitute and increase its military power.
To get out of the positional form at the current stage of warfare, first of all, it is necessary to: gain air superiority; breach mine barriers in depth; increase the effectiveness of counter-battery and electronic warfare; create and prepare the necessary reserves. It should be taken into account that the widespread use of information technology in military affairs and the rational organization of logistics support play a significant role in finding a way out of the positional form of warfare. The need to avoid transitioning from a positional form to a manoeuvrable one necessitates searching for new and non-trivial approaches to break military parity with the enemy